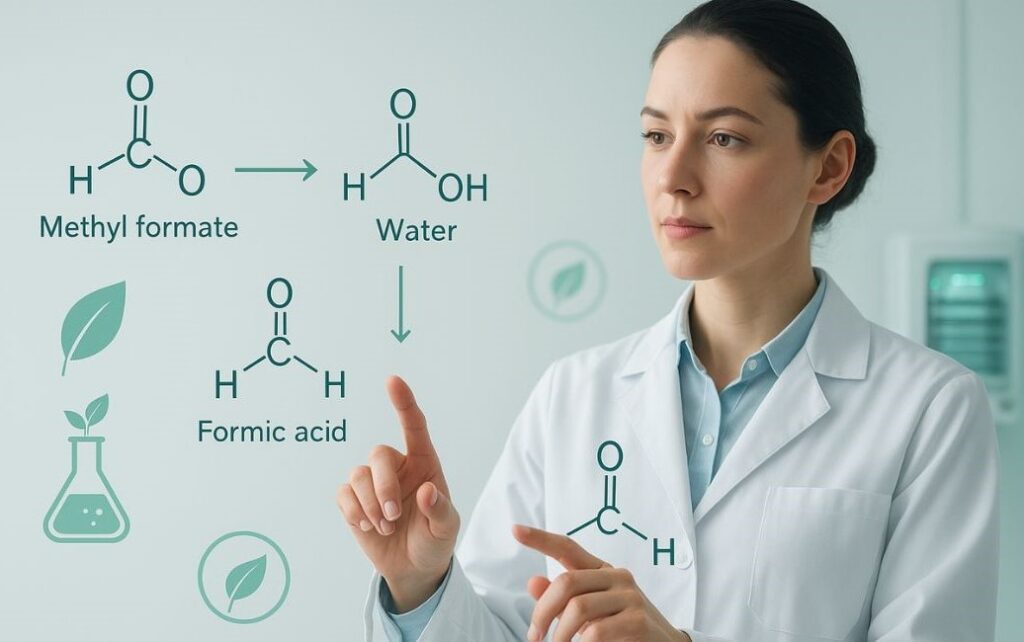
The formula hcooch ch2 h2o often confuses new learners in organic chemistry. It represents a reaction where methyl formate interacts with water (H₂O), leading to hydrolysis. In simple words, it explains how esters break down to give formic acid (HCOOH) and methanol.
This reaction matters because it connects to industrial chemistry, green energy, fuel cells, and even polymer synthesis. Understanding it helps explain both basic reaction mechanisms and modern sustainable applications.
- What Is HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O in Chemistry?
- The Basics of Methyl Formate Hydrolysis
- Why Is Formic Acid (HCOOH) Important?
- The Role of Methylene (CH₂) in the Reaction
- How Does Water (H₂O) Work in Hydrolysis?
- Industrial and Green Chemistry Applications
- Common Misconceptions in Chemical Nomenclature
- Reaction Mechanism and Conditions
- Environmental and Safety Considerations
- Case Study: Formic Acid Fuel Cells
- Conclusion
What Is HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O in Chemistry?
Many people ask: what is hcooch ch2 h2o and how is it used? It refers to the hydrolysis of methyl formate. When methyl formate meets water, a breakdown happens. This is an ester hydrolysis mechanism.
The process gives two products: formic acid (HCOOH) and methanol. Both have wide use. Formic acid has industrial applications, while methanol is important in fuel cells and green chemistry applications.
The Basics of Methyl Formate Hydrolysis
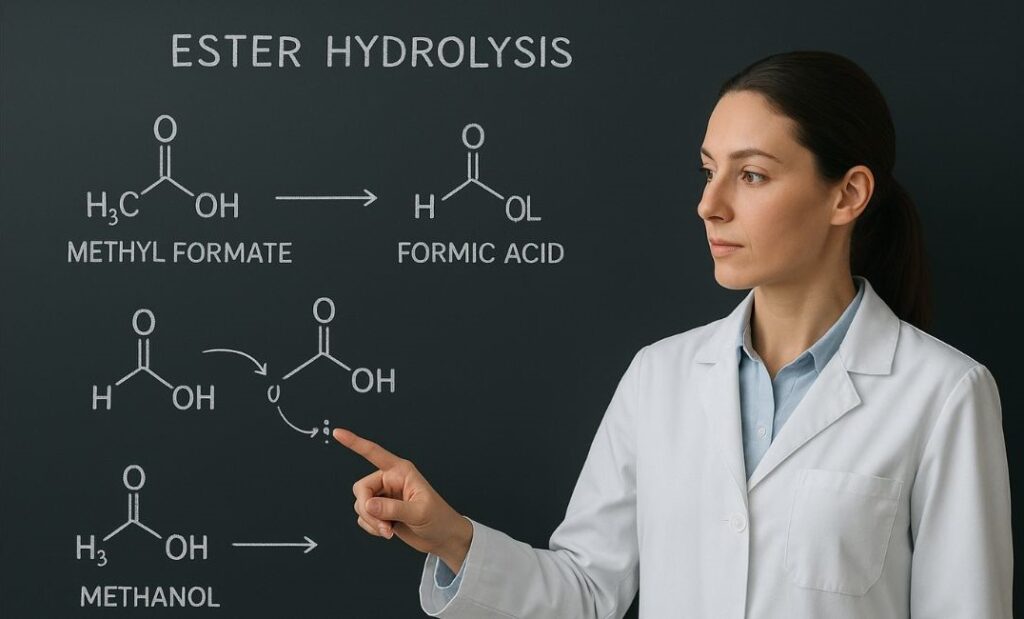
The key step is the protonation of ester. In acid-catalyzed reaction pathways, a proton transfer makes the ester functional group reactive. Then, water as nucleophile attacks the carbon.
The reaction kinetics in organic chemistry show that this step depends on pH-controlled chemical processes. Too much acidity or alkalinity changes the speed of the hydrolysis.
| Reactant | Product | Role in Chemistry |
| Methyl formate | Formic acid + Methanol | Starting ester compound |
| Water (H₂O) | Hydrolysis medium | Solvent roles in chemical reactions |
Why Is Formic Acid (HCOOH) Important?
Formic acid applications go beyond textbooks. It is used in textile dye fixation techniques, latex coagulation chemistry, and even as a formic acid hydrogen donor in fuel cells.
There are also environmental angles. The environmental impact of formic acid is lower compared to stronger acids, making it useful in environmentally friendly reagents and green chemistry principles.
The Role of Methylene (CH₂) in the Reaction
The CH₂ functional group is a special organic synthesis intermediate. It creates methylene bridge chemistry, which is vital in polymer cross-linking agents and plastic and polymer manufacturing.
In methylene intermediate reactions, the reactive organic systems often form new structures. For example, CH₂ insertion reactions lead to polymerization and resin synthesis.
How Does Water (H₂O) Work in Hydrolysis?
The role of water in ester hydrolysis reactions is central. Water as nucleophile attacks the carbonyl group. This is a nucleophilic substitution that leads to bond breaking.
At the same time, hydrogen bonding in water supports the solvent-mediated organic reactions. This makes hydrolysis in aqueous media possible and stable.
Industrial and Green Chemistry Applications
In industrial organic synthesis, the reaction is important for making agrochemical synthesis products, renewable industrial solvents, and polymer synthesis.
In green chemistry trends, circular chemistry from CO₂, bio-inspired catalysis, and renewable energy chemistry rely on such reactions. Green chemistry applications show how sustainable chemical alternatives can replace harmful reagents.
Common Misconceptions in Chemical Nomenclature
A lot of confusion exists when people ask: what is the hydrolysis of methyl formate? or mix hcooch=ch2 + h20 with hcooch+h2o. These are often misconceptions about chemical compounds.
Another misconception is about understanding non-IUPAC chemical formulas. For instance, some learners think hco2 stands for something different than formate ion. Proper names avoid mistakes in laboratory protocol.
Reaction Mechanism and Conditions
The ester hydrolysis mechanism depends on hydrolysis reaction conditions. Usually, an acid catalyst or a base catalyst is needed. These acidic conditions or pH control change the rate.
The reaction dynamics under nanoconfinement or with enzyme mimic catalysis are new research areas. They study reaction optimization via pH control and catalyst effects on ester hydrolysis.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Any reaction with volatile organics raises environmental safety issues. The environmental impact of volatile organics can cause air pollution. That is why safe handling of esters is needed.
Lab workers follow chemical safety and wear personal protective equipment (PPE). They rely on a safety data sheet (SDS) to avoid toxicity and other risks of chemical stability and volatility.
Case Study: Formic Acid Fuel Cells
One real-world example is formic acid fuel cells. These use formic acid as hydrogen donor in fuel cell membranes. The fuel cell membrane compatibility is studied with Pd²⁺ catalyst and Cu²⁺ catalyst.
This shows how formic acid methyl ester reactions can lead to green energy. It connects to renewable electricity, CO₂ recycling, and circular chemistry.
Conclusion
The reaction hcooch ch2 h2o is more than a formula. It explains esterification reactions, hydrolysis in acidic conditions, and the role of reactive intermediates in organic scaffold formation.
It also links to sustainability, green chemistry involving formic acid, and even fuel cells. So, when people ask why is hcooch ch2 h2o trending in organic chemistry?, the answer is clear. It matters for industry, environmental considerations, and the future of green energy.
Looking for more insights? Explore our blog for helpful and informative articles.
Disclaimer:
This content is written for educational and informational purposes only. We do not provide any kind of legal, financial, or medical advice, nor do we promote any type of investment. The information shared here is only a general overview.
FAQs
What is the common name for HCOOCH3?
The common name for HCOOCH₃ is methyl formate, an ester of formic acid and methanol.
What is another name for methyl formate?
Another name for methyl formate is formic acid methyl ester.
What is hcooch2ch3?
HCOOCH₂CH₃ is ethyl formate, an ester formed from formic acid and ethanol.
What is CH3COOCH3 also known as?
CH₃COOCH₃ is also known as methyl acetate, a common organic solvent.
What is CH3COOCH3 used for?
Methyl acetate (CH₃COOCH₃) is used as a solvent in paints, coatings, and adhesives.
What is sodium acetate used for?
Sodium acetate is used in textiles, heating pads, food preservation, and chemical buffers.